Touch screens have revolutionized the interactive way of electronic devices in recent years. We can control the appliances by only tapping, swiping, and pinching the screen. These devices include smartphones, tablets, laptops, and many industrial and medical applications.
But did you know different types of touch screens, including the “resistive touch screen”? Many industries devices use it as it is durable and rugged.
This article will explain resistive touch technology and how they work. We’ll also talk about the advantages and disadvantages of this technology. Furthermore, you will know their uses and future development.
After reading this article, you’ll understand what resistive touch screen is, how it works, and why it is essential today.
Page Contents
ToggleWhat is resistive touch screen?
A resistive touch screen panel has two layers coated with a transparent conductive material (Indium tin oxide) separated by a thin gap. The upper layer can bend as it is typically made of a flexible material like polyester or polycarbonate. The bottom layer is hard as it is made of glass or a similar rigid material.
When someone presses the screen with his finger or a stylus, the upper layer gets pushed down and touches the bottom layer. That will create an electrical circuit telling the devices where you touched. Then, the device will respond accordingly for the location of the point of contact.
Resistive touch screens have simple construction and operation compared to other types of touch screens. They are also cheaper than capacitive touchscreens. It is a good choice in applications where cost is a key factor.
Resistive Touchscreen Technology Types
According to the circuit layout, there are 3 main types of resistive touchscreen technologies: 4-wire, 5-wire, and 8-wire. Each structure determines the circuit’s cost, power consumption, durability, and sensitivity.
4-wire resistive touch panel
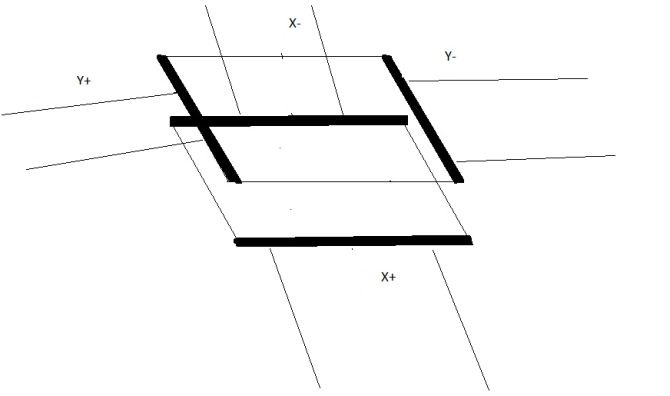
A 4-wire touchscreen panel contains two special parallel electrodes (“Busbars”) on each ITO (Indium tin oxide) layer of the touch screen. These bushbars are oriented perpendicular to another layer (see the figure).

Furthermore, the system controller uses a 4-wire flex cable connecting the busbars. These 4 wires are X+ (left), X- (right), Y+ (top), and Y-(bottom). Then, the controller can detect where and how much pressure is being applied.
The screen can determine the pressure level by measuring the resistance between the two ITO layers. That is the main advantage of a 4-wire touch screen.
This feature is helpful for applications that require more information than just the point of contact. The resistance decreases as the touch pressure (or the size of the depressed area) increases. For example, the touch screen could detect the size and force of the touch, which could be helpful in certain situations.
Overall, the 4-wire resistive touch screen is a valuable tool that can provide more information about the touch input than other types of resistive touch screens.
5-wire resistive touch panel
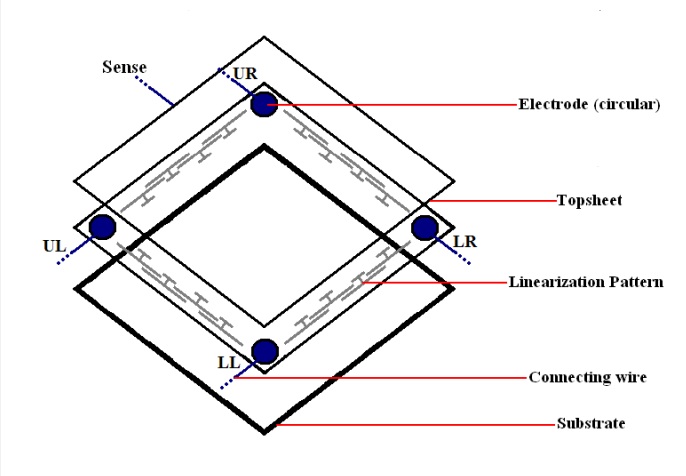
A 5-wire touchscreen panel locates four circular electrodes at each corner of the ITO layer of the bottom substrate. The conductive linearization pattern connects them for applying uniform voltage.
Meanwhile, 4 wires attach these electrodes. And the fifth “sense” wire is embedded in the top ITO layer. It can be sensing the electrode voltage.
The design of a 5-wire touch screen is simple and requires fewer circuit components. This advantage makes the 5-wire touch screen more durable.
8-wire resistive touch panel
An 8-wire resistive touchscreen panel is similar to the 4-wire layout, but each of the bushbars contains two wires. Suppose one of the wire pairs loses resistance over time. In that case, the second wire can still provide a secondary signal to the system controller.
As a result, the 8-wire sensing circuit is the most sensitive, precise, and stable resistive screen design. Compared to 4-wire or 5-wire resistive touch screens, 8-wire touch screens are more accurate and can detect smaller touch inputs. They are also less prone to errors and drift over time, making them more reliable for long-term use. However, they are more expensive to manufacture than other resistive touch screens.
4-wire and 5-wire resistive touch screens are the most popular and common technologies. They have low costs and simple interface electronics. Therefore, they share about 75% market. We can find them in various mobile applications, including industrial devices, medical machines and military applications.
Advantages of Resistive Touch Screens
Resistive touch screens have several advantages making them useful for specific applications.
Highly durable and rugged
Resistive touch screens are made of tough materials and have no moving parts. Therefore, they are less likely to be damaged by drops, impacts, or other physical stresses. That is important for industrial and military devices. They can still work well and withstand harsh conditions.
Cheaper
Resistive touch screens use simpler technology and fewer components. So manufacturers can produce them at low prices. And that is suitable for applications where cost is a primary consideration, such as retail point-of-sale (POS) systems.
High accuracy
Resistive touch screens use physical contact to address the point of touch. They can find the point precisely. This is helpful for things like medical equipment or scientific instruments.
Compatible with various input devices
You can press resistive touch screens with fingers, pens, and gloves. This is well-suited for environments where users must wear gloves for safety or hygiene. They are suitable for places like hospitals or food processing plants.
Suitable for use with gloves or styluses
Users can use styluses to write or draw on the resistive touch screen with precision. This feature is popular in applications like electronic signature pads or graphic design tablets.
Overall, resistive touch screens have several advantages, making them a popular choice in various industries. However, there are also some limitations to this technology. We will talk about this in the next section.
Disadvantages of Resistive Touch Screens
Though resistive touch screens have many benefits, they also have some disadvantages.
Do not support multi-touch
A resistive touch screen relies on physical contact. That makes it can only detect one touch at a time. Thus, it is hard to work with multi-touch.
Users cannot use two fingers to zoom in on a picture or rotate it. And it is hard to use some apps or games that need multiple inputs.
In contrast, capacitive touch screens work well with multi-touch. They can recognize multiple touch points simultaneously at a time.
Limited contrast, lower image quality
The layers of the resistive touch screen create a slight haze or distortion. That reduces the brightness and sharpness of the display. As a result, users are hard to see the image compared to other touchscreen technologies.
The screen material is more prone to damage
Compared to capacitive touch screens, the material of resistive touch screens is more prone to damage. Additionally, they use pressure to identify touches. That results in ease of scratched or cracked. That leads to reduced functionality or even complete failure.
Less sensitive
A resistive touch screen is less sensitive than other touch screen technologies, like a capacitive touch screen. You might have to press harder to get them to identify your touch. This results in slower response times and reduced accuracy.
Discomfort for long using
A resistive touch screen requires a certain amount of pressure to work. So users may feel uncomfortable to use for a long time. People having difficulty moving or using their hands are hard to control.
Despite these disadvantages, resistive touch screens are still prevalent in many industries and applications. They are easy to use and affordable. Meanwhile, they work well for situations where durability, accuracy, and versatility are essential considerations.
Devices Use Resistive Touch Screens
Resistive touch screens are affordable, durable, and easy to use. Many industries use them for different purposes. Here are some of the most common applications using these touchscreens:
Point of sale (POS) systems
Resistive touch screens are commonly used in POS systems in retail stores, restaurants, and other businesses. They allow for quick and easy data input and can withstand heavy usage.
Industrial controls
With resistive touch screens, industrial control panels can provide operators with a user-friendly interface for controlling machinery and monitoring processes.
Medical equipment
Resistive touch screens are easy to use and durable. Therefore, many medical devices, such as monitors, infusion pumps, and ventilators, use them.
Military and defense Devices
Resistive touch screens are a reliable and durable technology for military and defense applications. They can withstand extreme environments and be compatible with gloves. Therefore, they are an ideal choice for soldiers and personnel in the field.
Gaming devices
Gaming devices, like slot machines or video poker machines, also use these touchscreens. Then, they can offer a simple and intuitive interface for players to interact with the games.
Kiosks
With resistive touch screens, public information kiosks can give users access to information such as maps, directories, and event schedules.
Cars
Cars use them for displaying infotainment. They allow drivers to easily control the audio, climate, and navigation systems while keeping their eyes on the road.
Automated Teller Machines (ATMs)
With them, ATMs can provide a user-friendly interface for banking transactions.
Digital signage
Digital signage displays use them to provide users with interactive information such as menus, schedules, and promotions.
Overall, resistive touch screens are helpful in many industries because they are durable, affordable, and easy to use. They are an essential part of many devices and systems we use daily.
Conclusion
Resistive touch screens have been around for decades. They’ve proven to be reliable and strong for many uses. Furthermore, they are simple and affordable. People still use them in harsh environments or for precise applications.
However, as technology grows, some new ideas can improve resistive touch screens and expand their potential applications in various industries.
One cool idea is the “haptic feedback.” With that, you’ll feel a tactile response when touching the screen. You will have a good user experience.
Additionally, manufacturers are also developing thinner and more flexible resistive touch screens. That could make them more useful to some devices like smartwatches and bendable displays.
Resistive touch screens still work well in harsh environments, like factories or the military. But with the development of new technologies, they could be suitable in other places too.
For example, integrating haptic feedback could make them more suitable for consumer electronics such as smartphones and tablets. Additionally, developing thin and more flexibility could lead to their use in the automotive industry for curved displays.
Capacitive touch screens are popular in consumer electronics like smartphones. However, resistive touch screens still have advantages. They work even if you wear gloves or use something else to touch the screen.
In short, resistive touch screens are still a promising technology that is constantly improving. Compared with capacitive touch screens, they have strength and durability in extreme environments. Therefore, they are an excellent choice for industrial and military applications.
